Research
Overview
Our research interests lie at the intersection of materials science, biophysics, and biomedical engineering. Specifically, we focus on the predictive design, synthesis, and functionalization of fibrous proteins, including silk, elastin, collagen, and keratin, for the development of de novo designed stimuli-responsive and hierarchical biomaterials. These studies encompass a broad range of topics, including fundamental investigation related to protein structure-function relationships and self-assembly mechanism, as well as applied biomaterial studies related to drug delivery, tissue engineering, surface coating, responsive bio-actuator, and bio-electronics.
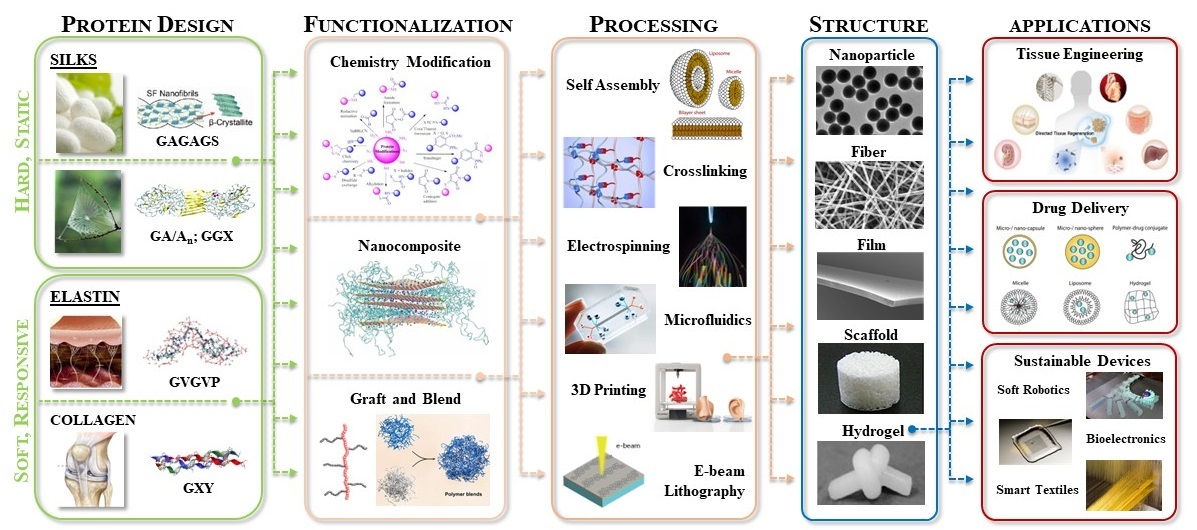
(1) Smart Material Design
– Development of protein-based biomaterials with pre-designed stimuli-responsive features for applications in biotechnology and medicine
The increasing demands of advanced healthcare have driven innovations in numerous functional biodevices. While many synthetic polymers demonstrated initial success for multiple clinical-related challenges, such as electronic skins, implantable devices, biosensors, and adaptive shape-memory materials, protein-based smart materials are still in high demand for biomedical applications due to their exquisite sequence control and thus precise chemistry, along with tunable mechanical properties, biocompatibility, and biodegradability.
Our lab aims to develop de novo designed protein-based biomaterials, which exhibit changes in one or more properties in response to an external trigger, to address biomedical needs for smart materials. A primary focus of our research is to construct stimuli-responsive yet robust protein libraries of silk-elastin-like proteins (SELPs) using an integrated genetic engineering + modeling approach. Our research also focuses on the functionalization and processing of SELPs using nano and microfabrication technologies, as well as exploiting the stimuli-responsive features of SELPs for applications in biotechnology and medicine, including on-demand drug delivery, smart tissue engineering, and soft robotics.
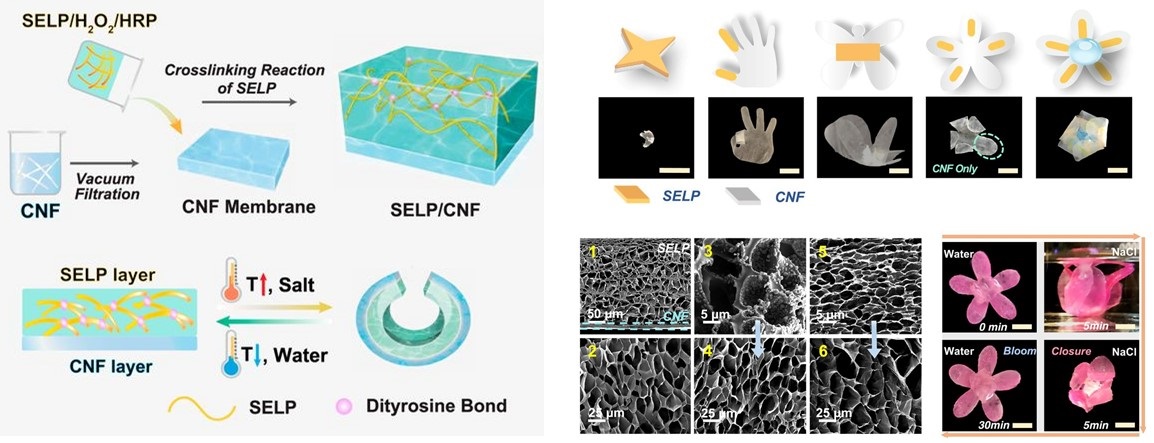
Related Papers:
- Bioinspired Genetic and Chemical Engineering of Protein Hydrogels for Programable Multi-Responsive Actuation, Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2024, 2401562.
- Stimuli-Responsive Composite Biopolymer Actuators with Selective Spatial Deformation Behavior, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2020, 117 (25), 14602-14608.
- Design of Multi-Stimuli Responsive Hydrogels using Integrated Modeling and Genetically Engineered Silk-Elastin-Like-Proteins, Advanced Functional Materials, 2016, 26 (23), 4113–4123.
(2) Musculoskeletal Tissue Regeneration
– Development of protein-based biomaterials for novel treatments and in vitro disease models of musculoskeletal system
Musculoskeletal diseases are the leading causes of chronic pain and physical disability, affecting millions of individuals worldwide. Despite recent advances in surgical and medication treatments, it remains challenging to fully restore the function of damaged musculoskeletal tissues. Therefore, designing advanced functional biomaterials, which can provide support, promote healing and restore function for musculoskeletal systems, has been paid increasing attention.
Our lab aims to develop protein-based hydrogels and porous scaffolds to address biomedical needs for novel treatments and in vitro disease models of knee osteoarthritis (KOA). A primary focus of our research is to synthesize and functionalize silk-based injectable hydrogels for the delivery and recruitment of cells to promote rapid cartilage and bone tissue regeneration. Our research also focuses on the development of in vitro disease model to identify the key attributes that cause KOA.
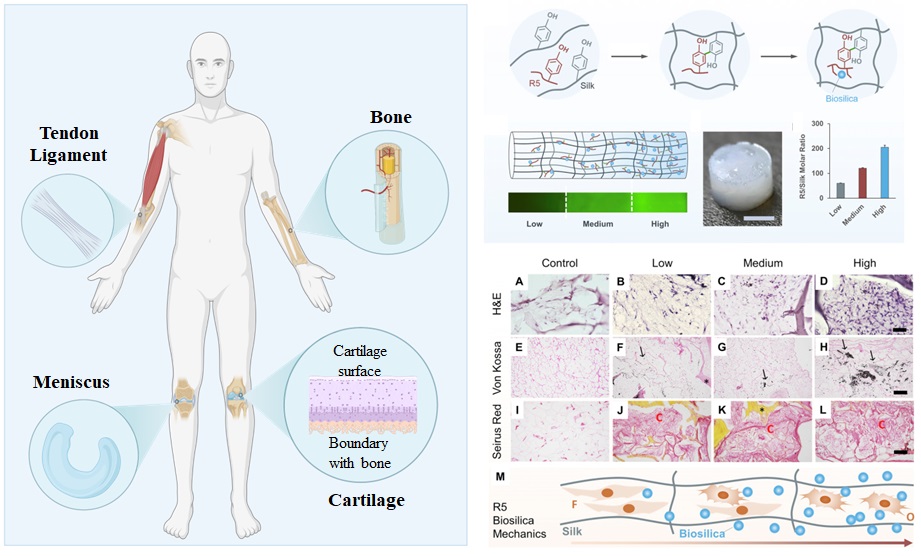
Related Papers:
- Advanced silk materials for musculoskeletal tissue regeneration, Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2023, 11, 1199507.
- Biomimetic Joint Paint for Efficient Cartilage Repair by Simultaneously Regulating Cartilage Degeneration and Regeneration in Pigs, ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13 (46), 54801.
- Multiscale Design and Synthesis of Biomimetic Gradient Protein/Biosilica Composites for Interfacial Tissue Engineering, Biomaterials, 2017, 145, 44-55.
(3) High Throughput Screening of de novo Designed Functional Proteins
– Development of protein high-throughput synthesis platform and advanced processing strategies for bionanotechnologies
Conventional material design strategies have focused on the rationale design of polymers followed by the characterization of these new or modified polymers for structure-function features to match specific goals. This strategy is conducted in an iterative fashion, leading to trial-and-error outcomes and relatively long timeframes to achieve specific functional goals. There remains an unmet need for a more efficient strategy to discover new functional biomaterials.
Our lab aims to develop new methods to synthesize and fabricate tailored biomaterials with tunable functional properties for bionanotechnologies. A primary focus of our research is to develop a robust high-throughput biomaterials screening strategy for the rapid and efficient discovery of new functional proteins, whereby synthesis and function are directly linked early on in the discovery process to assure a more rapid and efficient outcome. Our research also focuses on using advanced processing strategies, such as microfluidics and 3D printing, to fabricate sustainable biomaterials.
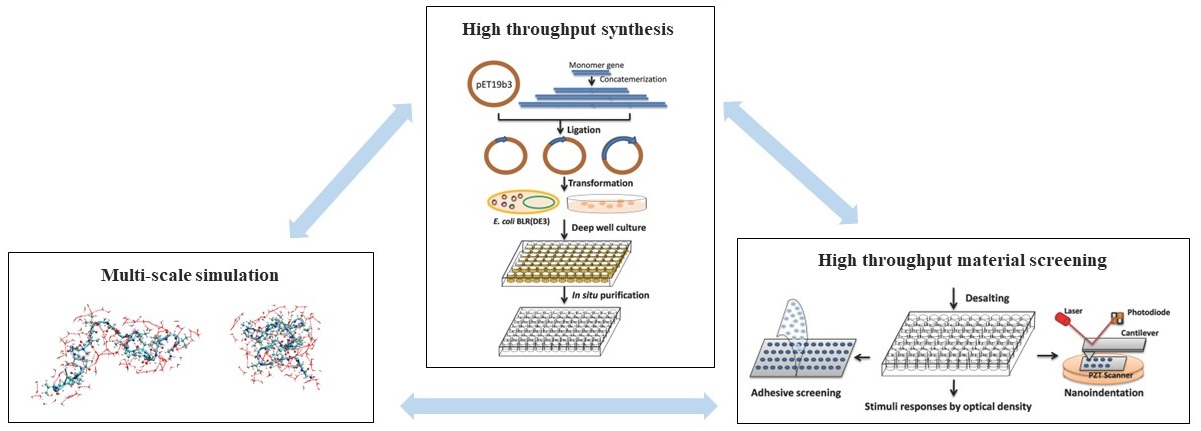
Related Papers:
- Thermo- and Ion-responsive Silk-Elastin-Like Proteins and Their Multiscale Mechanisms, Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2022, 10, 6133-6142.
- Synergistic Integration of Experimental and Simulation Approaches for the de novo Design of Silk-based Materials, Accounts of Chemical Research, 2017, 50 (4), 866-876.
- High Throughput Screening of Dynamic Silk-Elastin-Like Protein Biomaterials, Advanced Functional Materials, 2014, 24 (27), 4303-4310.
